What Is a Contour Interval?
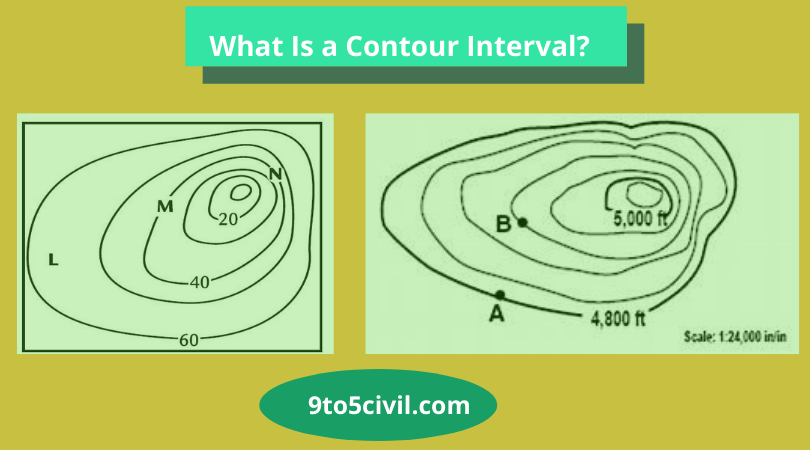
Contour Interval Definition: A contour interval is a vertical height or a difference in elevation between contour lines in a topographic map. Usually, there are different contour intervals for the different vertical distances on maps.
Define Contour interval is a line that connects the different points of equal height at the surface of the earth.
Example: The level of the calm water surface is the same. If its R.l is 200 mt, then 200 mt shows the contour.
A contour line is a line on a map representing an imaginary line on the earth’s surface, with all points at the same height as the datum plane, usually considered the sea surface as a datum plane.
Also Read: What Is the Estimate? | Type of Estimate | Advantage & Disadvantage of Estimate
Contour Lines
Contour lines are contours drawn on a map connecting points of equal elevation. Every Contour lines show elevation and the shape of the terrain.
The increasing order of contour lines represents the mountain’s surface, and the decreasing of contour intervals represents the cover of the valley or ridge.
Index Contour
An index contour is one of the ways that vertical height is demonstrated on a topographical map.
One contour line shown on the map is kept at a higher vertical difference than other contour lines for ease of identification.
Also Read: What Is False Work? | Types of Falsework | Causes of Falsework Failures
What Is a Contour Gradient?
All lines connecting points of uniform slope in a mountainous area are called contour gradient.
Use of Contour Map
- Maps are drawn with the help of contours.
- With the help of contour, knowing the topography of the ground helps.
- Military tactics can be created using Contour.
- Contour is used to select the location for the construction of dams, bridges, etc.
- The reservoir’s capacity helps to know from the contour map.
- The contour gradient is drawn from the contour map.
- The area of the closed discharge field is be determined from the contour map.
- Contour maps can determine the area of a reservoir, which area lies in the lower part.
- Used to draw a cross in any direction from the contour map
- Very useful for determining line length of the road, pipeline, sewer line, railway line, etc.
- The contour map helps to know the height of a given two points.
Also Read: What Is Fire Escape Staircase? | Types of Fire Escaping Stairs | Fire Escape Staircase Regulations
Characteristics of Contour
- The vertical distance of all the points on the contour line is equal.
- Two contour lines of different heights do not intersect each other. But the contour line for overhanging cliff intersects each other.
- But if the sloping of the ground is high, then the contour lines are far apart from each other.
- And if the slope of the ground is low, then the contour lines are very close to each other.
- The contour lines of a plain are straight and parallel to each other.
- While the contour lines of the elevated ground are crooked and irregular
- If the slope of the plains is uniform. If so, the contour lines are at equal distances.
- As the height increases from the outside to the inside, it shows a hill mark in closed contour lines.
- If the height decreases from the outside to the inside in closed contour lines, it indicates a pit mark.
- The lower part of the hill is called the saddle. Four pairs of contour lines represent it.
- Contour lines of similar height do not intersect.
- The contour line on the map ends at the point where it started.
Also Read: What Is a Dead Load? | What Is Live Load? | Difference Between Dead Load Vs Live Load
Contour Interval Depends on the Following Factors.
1. Nature of Ground:
But if the sloping of the ground is high, then the contour lines are far apart from each other.
And if the slope of the ground is low, then the contour lines are very close to each other. The contour lines of a plain are straight and parallel to each other.
2. Scale of the Map:
The smaller the scale of the map, the higher the contour spacing. The larger the scale of the map, the smaller the contour spacing.
3. Purpose of Surveying
3.1. Topographical Survey: Determining natural features rivers, lakes, forests, etc., and artificial features road, railway, cities, villages, etc.
3.2. Cadastral Survey:
- To determine the property line.
- To calculate the area.
- To determine the boundary of state and municipality.
3.3. City Survey:
- To determine the alignment of city roads.
- To determine the alignment of water lines and sewer lines.
3.4. Marine Survey:
- To know the discharge of the river.
- Beach and river survey.
- To measure the flight of the coast.
3.5. Military Survey:
Surveys are conducted on military matters.
4. Area of Surveying
The smaller the area of surveying, the smaller the contour interval distance.
The larger the area of surveying, the high the contour interval distance.
The Contour Intervals for Different Purposes Are Kept as Follows
| Sr.No. | Scale | Description | Contour Interval |
| 1 | Large Scale | Building Site | 0.2 to 0.5 |
| 2 | Medium Scale | Town planning | 0.5 to 5.0 |
| 3 | Small Scale | Cadastral Survey | 5 to 10 |
Also Read: What Is Concept Drawings? | Architecture Concept Drawing | Types of Drawings for Building Design
Method of Contouring
The method of contouring occurs in two ways,
- Direct method
- Indirect method
1. Direct Method
In this method, the points connecting the points of equal height are drawn using a dumpy level machine.
In this method, the level machine is fixed in the center, then the machine’s leveling is done than reading is done on the benchmark first. Then reading is done on the ground. Suppose the benchmark is R.L 100 mt, and It comes with a reading of 1.40 mt.
We now have to draw a ground contour line of 100 mt. So that the staff reading of each point on the 100 mt contour line is 1.4 mt. Thus marking the different points with a 1.40 mt reader on the ground and connecting them becomes a contour line with 100 mt R.L.
Also Read: What is Tributary Area? | Tributary Area in Column | How to Calculate Tributary Areas
2. Indirect Method
This method is faster and cheaper than the direct method. With less effort from an INDIRECT METHOD,
contour lines can be drawn on the map. In this way, relative heights are determined by level machine keeping staff at different points.
There are three ways of the Indirect method
- Method Of Squares.
- Method Of Cross-Sectioning
- Method Of Tacheometry.
What Is Reading a Topo Map?
Studying a topo map of a familiar area is a great way to learn how to match terrain features with the contour lines on a map. Index contour lines: Every fifth contour line is a thicker, “index” line. At some point along that line, its exact elevation is listed. You find the contour interval for your map in its legend.
Contour Interval
A contour interval is a vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing.
Contour Lines
Contour lines are lines drawn on a map connecting points of equal elevation, meaning if you physically followed a contour line, elevation would remain constant. Contour lines show elevation and the shape of the terrain. They’re useful because they illustrate the shape of the land surface-its topography. Moreover, topographical surveyors in Edmond know how to do it.
Contour Interval on Topographic Map
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is a vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. Sharp contour points indicate pointed ridges.
What is the Contour Interval of the Map?
A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing.
Contour Lines and Contour Intervals
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line.
Contour Index
Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing. If the numbers associated with the contour lines are decreasing, there is a decrease in elevation.
Uses of Contour Intervals in Surveying
A higher contour interval is used for a large area and small contour interval for small area. In a large map, index contour lines are less to keep it simple to read the map easily. In this case, to find out the intermediate points elevation, contour intervals are used.
What Is the Contour Interval Equal To?
Divide the difference in elevation between the index lines by the number of contour lines from one index line to the next. In the example above, the distance 200 is divided by the number of lines, 5. The contour interval is equal to 200 / 5 = 40, or 40-unit contour intervals.
What Is the Purpose of Contour Interval?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines.
What Is the Difference Between Contour Interval and Scale?
Scale and Contour Interval. Contour Interval: The contour interval on a topographic map is the vertical distance between one contour line and the next. The scale of a WWI military map is usually conveyed by a representative fraction, graphic line or both.
What Is a Contour Index?
Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing.
What Is the Factors Affecting Contour Interval?
- The Scale of The Map: The contour interval is inversely proportional to the scale of the map. If the scale is small, the contour interval should be large and vice versa.
- Nature of The Ground: The general terrain of the area determines the contour interval. For a flat area, the contour interval should be small. For sloping or undulating terrain, the chosen contour interval should be large
- Purpose and Expansion of the survey work: If surveying work is to be used for precise and detailed calculations, then the small contour interval should be chosen and a large contour interval is chosen for the following cases: For catchment areas, To the reservoir, For location survey.
- Time available and Eligible Expenses for field and office work: A large contour interval should be used if the time available for survey work is less. The small contour interval, survey work, and plotting need to be more precise. For a small contour interval, the money needed will also be more as the field and office work will be larger.
Types of Contour Lines
There are 3 kinds of contour lines you’ll see on a map: intermediate, index, and supplementary.
- Index lines are the thickest contour lines and are usually labeled with a number at one point along the line. This tells you the elevation above sea level.
- Intermediate lines are the thinner, more common, lines between the index lines. They usually don’t have a number label. Typically one index line occurs for every five intermediate lines.
- Supplementary lines appear as dotted lines, indicating flatter terrain.
What Is a Contour Interval Apex?
Where contour lines form a “V” the apex of the “V” points uphill. The contour interval is the difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines. The lowest elevation on the map is about 1150 feet (south edge of the map).
Why Are Contour Lines Used?
The purpose of contour lines is to represent the tridimensional shape of the terrestrial surface on a bidimensional map. Contour lines are the intersection of an horizontal plane parallel to the reference level and the topographical surface to describe. Consequently: Contour lines are always closed curves.
How Do Contour Lines Work?
The feature that makes this possible is contour lines: Contour lines indicate the steepness of terrain. Contour lines connect points that share the same elevation: Where they’re close together (they never intersect), elevation is changing rapidly in short distance and the terrain is steep.
What Shape Are the Contour Lines?
At a stream junction, contour lines form a “M” or “W” shape. This can be interpreted as two “V-shaped contours intersecting.
What Is Contour Interval on a Topographic Map?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line.
Contour Interval Formula
The contour interval is equal to 200 / 5 = 40, or 40-unit contour intervals. If, on the other hand, the elevation difference between the index lines were 100 feet, the contour interval would be 100 / 5 = 20 or a 20-unit contour interval.
Contour Lines Geography
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines.
How Do You Read Contour Intervals on a Topographic Map?
- Index lines are the thickest contour lines and are usually labeled with a number at one point along the line. This tells you the elevation above sea level.
- Intermediate lines are the thinner, more common, lines between the index lines. They usually don’t have a number label. Typically one index line occurs for every five intermediate lines.
- Supplementary lines appear as dotted lines, indicating flatter terrain. If you’re looking at an index line, it’s easy to read the elevation because it is clearly labeled. However, interval lines are somewhat trickier. To determine their elevation, you’ll need to know the contour intervals.
What Is a Contour Interval Example?
A topographical map of an area near Denver might have index contours of 5,000′, 5,100′ and so on with a contour interval of 20 feet. This means that there would be five “spaces,” and four non-index contour lines, between each index contour. Often, index points are given along with index contours.
How Much Is the Contour Interval on a Topo Sheet?
The elevation difference or vertical distance between two adjacent contour lines would be 20 meters (100 : 5 = 20). Therefore the contour interval is 20 meters.
How Do You Find the Contour Interval on a Map?
Contour interval calculator:
Contour intervals tell you the change in elevation between any two contour lines. You can find the contour interval in the map key, usually located underneath the scale of the map at the bottom center.
What Are the 5 Rules of Contour Lines?
- Rule 1 – every point of a contour line has the same elevation.
- Rule 2 – contour lines separate uphill from downhill.
- Rule 3 – contour lines do not touch or cross each other except at a cliff.
- Rule 4 – every 5th contour line is darker in color. This is an INDEX contour line.
- Rule 5 – Contour lines are closer together in steep terrain and farther apart in flat areas.
Where Is the Contour Interval on a Map?
Contour intervals tell you the change in elevation between any two contour lines. You can find the contour interval in the map key, usually located underneath the scale of the map at the bottom center.
How Do You Find the Index Contour?
Find the Index Contour. Before you ever start analyzing contours, you should determine the contour interval which is found in the bottom center of the map. To determine the elevation of a point, you must have a reference line from which to start. This reference line is an index contour.
What Color Is an Index Contour Line?
To make topographic maps easier to read, every fifth contour line is an index contour. Because it’s impractical to mark the elevation of every contour line on the map, the index contour lines are the only ones labeled. The index contours are a darker or wider brown line in comparison to the regular contour lines.
Why Is an Index Contour Important?
Index contours help the map reader get a better feel for the topography of an area. Every 100 ms above sea level, the contour is a darker, thicker brown and is also labelled with the elevation, while the others are lighter, thinner and have no label.
What Are Index Contour Lines on a Topographic Map?
Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing. If the numbers associated with the contour lines are decreasing, there is a decrease in elevation.
What Is the Contour Interval on the Map?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line.
What Is Meant by the Term Contour Interval?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line.
What Are the Uses of Contour in Surveying?
- It depicture slope and size of different landforms on map.
- It provides a complete and clear image of the land and the surrounding area.
- By reading contour intervals it is easy to sort out the different elevations of the landscape.
- It provides the basis for coloring method.
What Does a Contour Interval Do?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. If the numbers associated with specific contour lines are increasing, the elevation of the terrain is also increasing.
What Is the Contour Interval Used on This Map?
A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line.
Why Are Contour Lines Useful?
Contour lines are useful because they allow us to show the shape of the land surface (topography) on a map. The two diagrams below illustrate the same island. The diagram on the left is a view from the side (cross profile view)such as you would see from a ship offshore.
What Is an Important Part of a Topographic Map?
Topographic maps give the user the ability to view a three-dimensional landscape on a two-dimensional map. One who is able to read a topo map can identify the elevation and location of valleys, peaks, ridges, and other land features.
What Are Four Main Uses of Topographic Maps?
Topographic maps have multiple uses in the present day: any type of geographic planning or large-scale architecture; earth sciences and many other geographic disciplines; mining and other earth-based endeavours (such as planning and constructing ponds); and recreational uses such as hiking or, in particular, orienteering, which uses highly detailed maps in its standard requirements.
What Is the Shape of Contour Lines?
Instead, contours form closed loops. These loops follow the shape of the land, and may extend past the edge of the map. Closely spaced contours indicate a steep slope, whereas contours that are spaced far apart indicate a gentle slope or almost flat surface.
How Do You Find the Height of a Contour Line?
Put simply, contour lines mark points of equal elevation on a map. If you trace the length of a line with your finger, each point you touch is the same height above sea level. If you were to walk the path of a contour line in real life, you would remain at the same elevation the whole hike, never traveling up or down.
How Do You Measure the Height of Land on a Map?
On the map, hover over a spot and click a starting point for your measurement. Then, hover over another spot and click an end point. The measurement will show up in the “Ruler” window.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Caisson Foundation | Use of Caisson Foundation | Type of Caisson Foundation | Advantages & Disdvantagesof Caisson Foundation
- Slump Test | Procedure of Slump Test | Advantage of Slump Test | Disadvantage of Slump Test
- What Is Pitched Roof? | Types of Pitched Roof | Advantage & Disadvantage of Pitched Roof
- What Is False Work? | Types of Falsework | Causes of Falsework Failures
- Sheep Foot Roller | Characteristics of Sheep Foot Roller | Advantage & Disadvantages of the Sheep Foot Roller
 Skip to content
Skip to content